在 ConvLab2 01. Agenda-based User Simulator 中, 我们介绍了基于 Agenda 的用户模拟器.
今天我们来介绍一个基于神经网络的端到端的用户模拟器: HUS.
HUS, 全称 Hierarchical User Simulator, 是 2018 年 Izzeddin Gur, Dilek Hakkani-Tur, Gokhan Tur, Pararth Shah 等人在论文 User Modeling for Task Oriented Dialogues 提出的用户模拟器. 当时4位作者都在 Google AI 工作.
User Modeling for Task Oriented Dialogues
任务型对话系统(Task Oriented Dialogue System, 简称 TOD) 是以人机交互的形式帮助用户完成目标 (accomplish their goal).
从TOD 架构上看, 可以将 TOD 的研究划分为两大类:
- Pipeline architecture
- end-to-end architecture
在 TOD 中, User Simulator 主要用于对话系统(或其各个模块) 的评估和训练. 整体而言, User Simulator 主要作用有:
- 辅助训练 TOD. 如 Asri et al [^1], Baolin Peng et al [^2] 及 Paul Crook et al [^3] 等实验了使用 seq2seq 模型构建的用户模拟器来训练 Dialogue Policy 模型
- 辅助评估 TOD. 使用 Simulator 模拟用户与 TOD 交互, 可以得到 User Goal 的 EM (Exact Matching) 和 PM (Partial Matching) 指标等.
HUS 是 User Simulator 的一种, 它借鉴了端到端 TOD 的设计思想, 也提供了一种端到端的 User Simulator. 具体地, HUS 利用了如下这些技术:
- seq2seq
- hierarchical model
- variational method
- goal regularization approach
seq2seq
seq2seq 是 2014 年 Google 的 Ilya Sutskever, Oriol Vinyals 及 Quoc Viet Le 等人在论文 Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Network 中提出的一种序列生成模型, 可以用在 NMT, NLG, QA 等多个 NLP 领域.
几乎在同一时期 (事实上比 Seq2seq 更早一些), Kyunghyun Cho, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Fethi Bougares, Holger Schwenk, Yoshua Bengio 等人在论文 Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation 中提出了 Encoder-Decoder 框架.
两篇论文采用了相似的系统架构, 不同点在于 Encoder-Decoder 论文使用了 GRU (当时论文中还没有称之为 GRU), 而 Seq2seq 则使用了 LSTM.
一般地, 除了特别声明, 我们认为 seq2seq 与 Encoder-Decoder 架构是同义词.
hierarchical model
Hierarchical model 指的是, 相关研究有:
- A Hierarchical Neural Autoencoder for Paragraphs and Documents, Jiwei Li, Minh-Thang Luong, and Dan Jurafsky, CoRR, vol. abs/1506.01057, 2015.
- A Hierarchical Recurrent Encoder-Decoder For Generative Context-Aware Query Suggestion, Alessandro Sordoni, Yoshua Bengio, Hossein Vahabi, Christina Lioma, Jakob Grue Simonsen, and Jian-Yun Nie, CoRR, vol. abs/1507.02221, 2015.
- A hierarchical latent variable encoder-decoder model for generating dialogues, Iulian Vlad Serban, Alessandro Sordoni, Ryan Lowe, Laurent Charlin, Joelle Pineau, Aaron C. Courville, and Yoshua Ben- gio, CoRR, vol. abs/1605.06069, 2016.
hierarchical, “按等级划分的; 等级制度的; 分层的; 分等级的”
- [adj] A hierarchical system or organization is one in which people have different ranks or positions,depending on how important they are.
hierarchical由hierarch+ 形容词后缀-ical构成.
hierarch来源于希腊词汇hierarkhia, 含义是 “one who rules in holy things” (“大主教; 祭司长; 统治集团首领”).
Hierarchical Model 也称为 Multi-Level model, 最常用的有:
- Hierarchical Linear Model, 层次线性模型 (HLM)
- Hierarchical Bayesian Model, 层次贝叶斯模型, 也称为贝叶斯网络
- Hierarchical Neural Network, 层次神经网络
层级模型使用了多个模型, 数据会先由底层模型处理, 其处理结果作为高层模型的输入特征进一步处理, 多级模型协作并联合训练.
HUS 中使用了
variational method
Variational Method / Variational Approach, 一般翻译为 “差分法; 变分法”, 在机器学习/深度学习模型中的典型使用是 Variational Auto-Encoder, 如:
- Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes, Diederik P Kingma, Max Welling, 2013
- Variational Recurrent Auto-Encoders, Otto Fabius, Joost R. van Amersfoort, 2014
HUS
在开始正式介绍 HUS 之前, 再次介绍一下 User Simulator 中的一些基本概念.
User Simulator 建模可以认为是 Dialogue System 的逆问题 (inverse problem), 其目标是根据 User Goal 和 系统响应 System Turn (可以是 System Action (Pipeline 架构), 也可以是 System Utterance (E2E 架构)) 来生成合适的 User Turn.
这里 User Goal 是一个 集合 及 一组预定义的用户个性 (User Personality, 可以是 aggressive / cooperative 等描述性词语, 也可以是自然语言描述的段落 ).
System Turn / User Turn 一般使用 Dialogue Action 来描述. Dialogue Action 可以表示为一组 构成的集合 (当处理 single domain 对话时, 可以省略 domain 元素).
问题简化
HUS 将 Slot Value 简化为 五个值.
数据序列化问题
User Simulator 的部分输入数据是结构化数据, 如 User Goal / System Action 等, 需要使用一定的方法将这些结构化数据编码为序列. 论文使用了 Grammar as a foreign language, 2014 给出的序列化方法, System Actionconfirm(movie=ValueInGoal, time=ValueInGoal)会被序列化为"confirm", "(", "movie=ValueInGoal", "time=ValueInGoal", ")"序列.
基于上述概念, User Simulator 的形式化建模如下:
即在给定 User Goal 和 System Turn 序列 的条件下, 生成合适的 User Turn .
HUS 基础模型
HUS 基础模型主要由四部分构成
- User Goal Encoding
- System Turn Encoding
- Dialogue History Encoding
- User Turn Decoding
其结构如下图所示
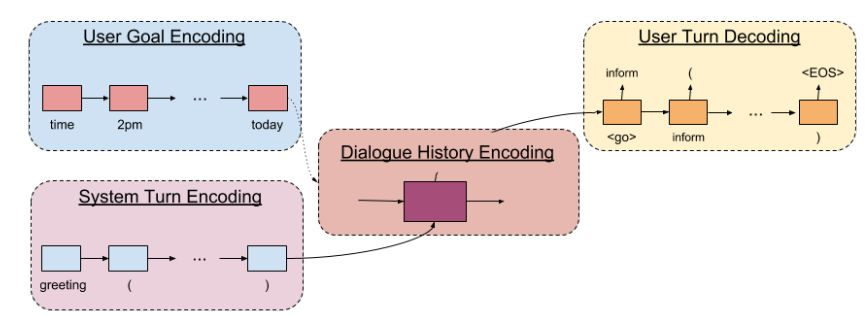
层级编码器
对于序列化后的 User Goal , 首先会经过一个 Embedding 层得到序列向量 , 然后经过 User Goal Encoder, 得到 User Goal 的隐层表示 , 即:
同理, 第 t 轮的 System Turn 可以得到隐层表示 , 即:
结合 及 , 使用 Dialogue History Encoder 可以得到 Dialogue History 的隐层表示, 即:
User Turn 解码器
HUS 使用了一个 RNN 来解码 User Turn, 第 t 轮的 User Turn 解码过程如下:
HUS 优化模型
VHUS
UHUSReg
ConvLab2 实现
参考文献
[^1]: Layla El Asri, Jing He, and Kaheer Suleman, “A sequence-to-sequence model for user simulation in spoken dialogue system”, CoRR, vol. abs/1607.00070, 2016
[^2]: Baolin Peng, Xiujun Li, Lihong Li, Jianfeng Gao, Asli Celiky- ilmaz, Sungjin Lee, and Kam-Fai Wong, “Composite task-completion dialogue system via hierarchical deep reinforcement learning”, arxiv:1704.03084v2, 2017.
[^3]: Paul Crook and Alex Marin, “Sequence to sequence modeling for user simulation in dialog systems”, in Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Commu- nication Association (INTERSPEECH 2017), 2017, pp. 1706– 1710.